Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) has gained attention as a functional food due to its high fiber content and potential health benefits. It is often used as a natural laxative and a source of omega-3 fatty acids. This article explores the benefits, potential uses, and considerations of flaxseed, particularly for lactating mothers.
Nutritional Benefits of Flaxseed
Flaxseed
is rich in:
✅ Nonabsorbable fiber – Promotes digestive health and helps with constipation.
✅ Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) – A plant-based omega-3 fatty acid that plays a role in
cardiovascular health.
✅ Lignans – Natural compounds with antioxidant properties that may support hormonal
balance.
Flaxseed Oil and Omega-3 Conversion
Flaxseed oil is a concentrated source of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). However, the body only partially converts ALA into docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), which are essential for brain and heart health. Since DHA is crucial for infant development, lactating mothers should rely on direct sources of DHA (such as fatty fish or marine oils) instead of flaxseed oil alone.

Flaxseed and Breastfeeding
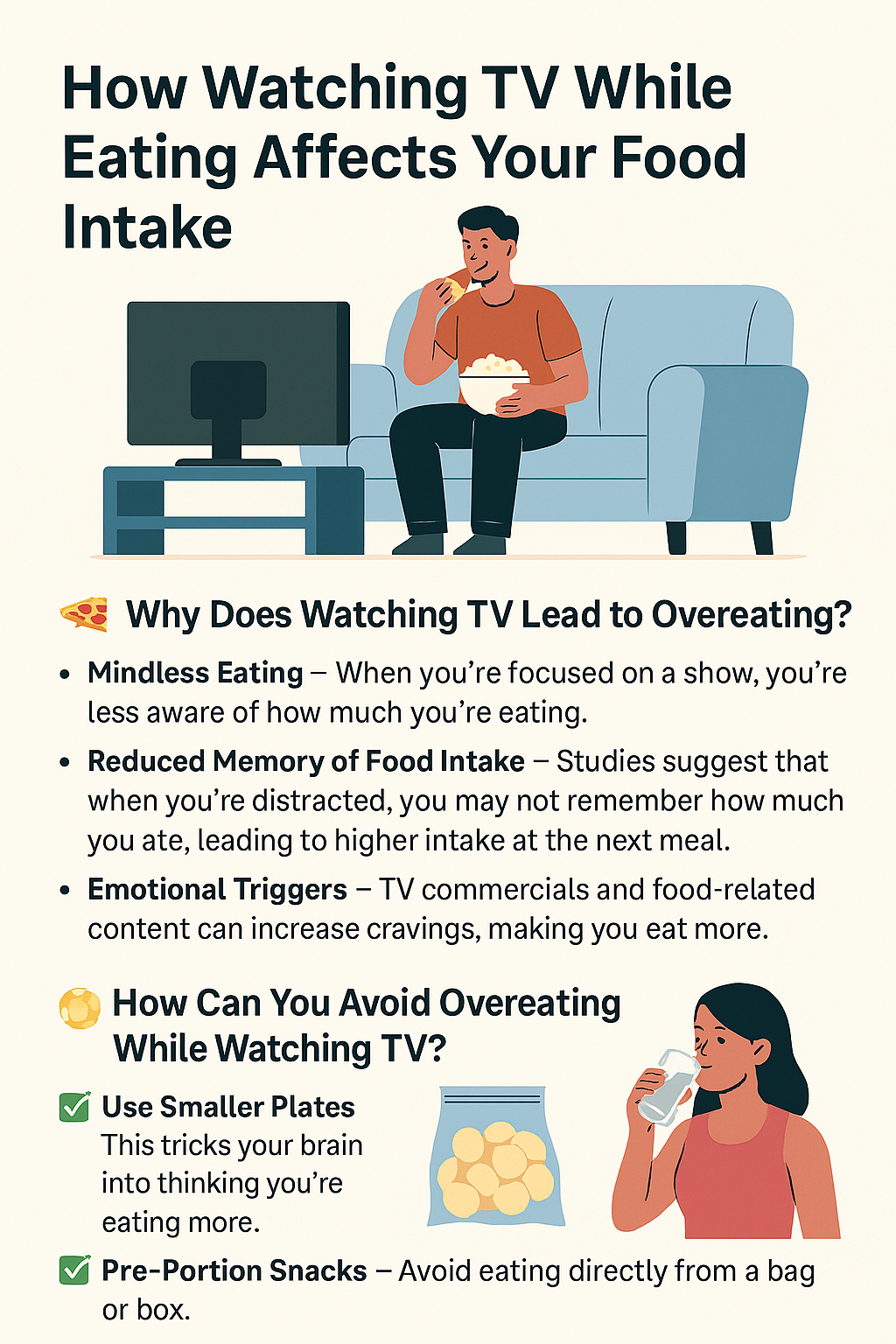
Several
factors may explain why children and adolescents experiencing depression turn to food for
comfort:
Considerations and Safety
⚠
Limited Data on Infants – While flaxseed is well tolerated in adults, research on its effects in
infants is limited.
⚠ Potential Allergic Reactions – Some individuals may experience allergic skin reactions.
⚠ Quality of Supplements Varies – Dietary supplements are not strictly regulated, and actual
ingredient amounts may differ from labels.
Conclusion
Flaxseed is a nutritious food with digestive and cardiovascular benefits, but it should not be relied upon as a primary omega-3 source for lactating mothers. For those seeking to increase DHA intake, marine-based sources are more effective. Always consult a healthcare provider before adding flaxseed supplements to your diet, especially during pregnancy and lactation.