What Defines a Healthy Weight?
A healthy weight varies significantly between individuals and depends on multiple factors including age, gender, genetics, body composition, and medical history. While Body Mass Index (BMI) remains a commonly used screening tool (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared), it has limitations as it doesn't distinguish between fat and muscle mass. Other important measures include waist circumference and body fat percentage.
The Evolution of Weight Guidelines
Early weight standards
like the 1943 Metropolitan Life Insurance tables provided generalized recommendations but had
significant limitations:
Why Weight Management Matters
Maintaining stable
weight in adulthood helps prevent:
Research shows that adults typically gain 1-2 pounds annually after age 20, with significant
health consequences:

The Obesity Paradox: Explained
Some studies suggesting overweight may be protective often fail to:
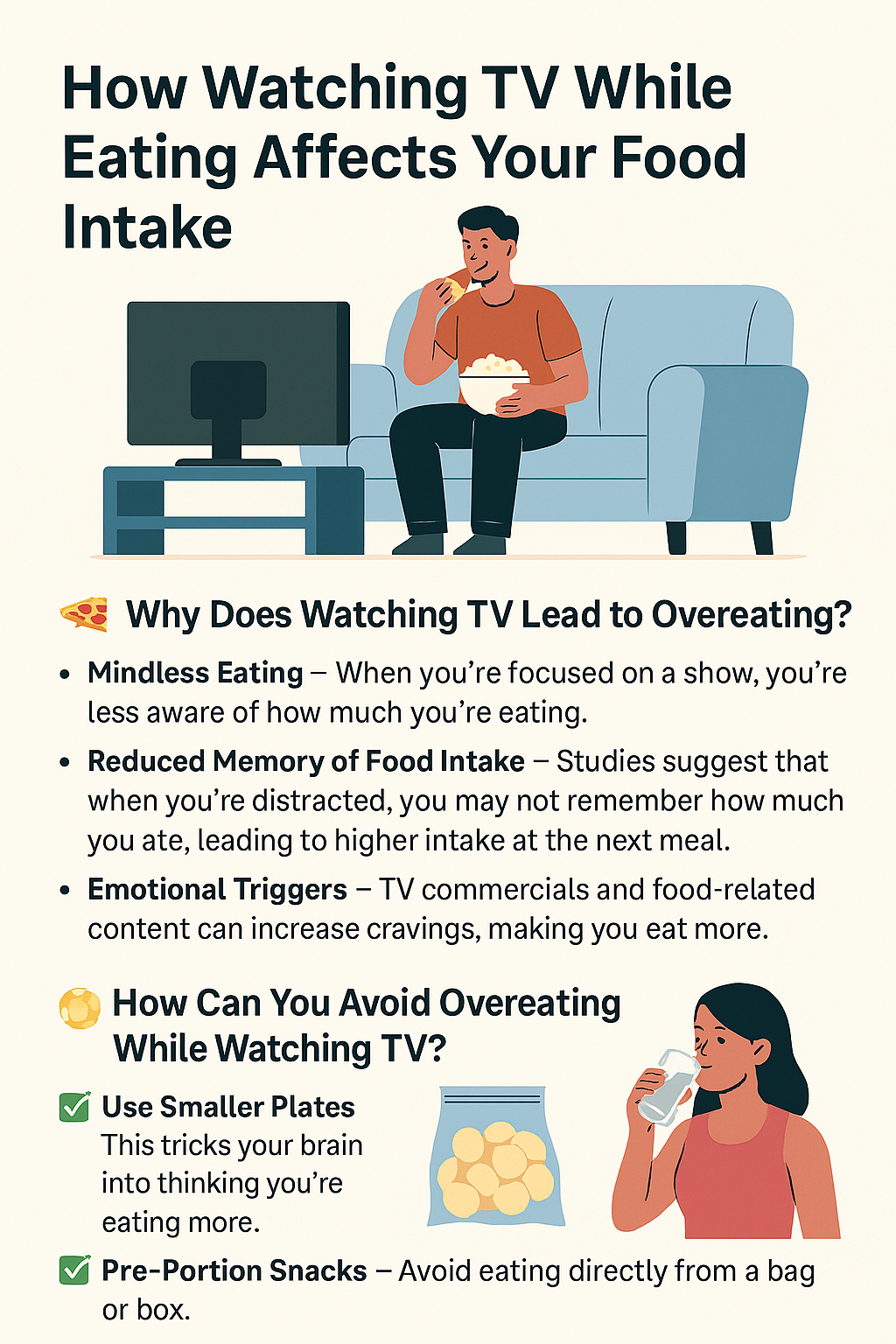
Key Contributors to Weight Gain
The Power of Modest Weight Loss
Losing just 5-10% of
body weight can:
Practical Recommendations