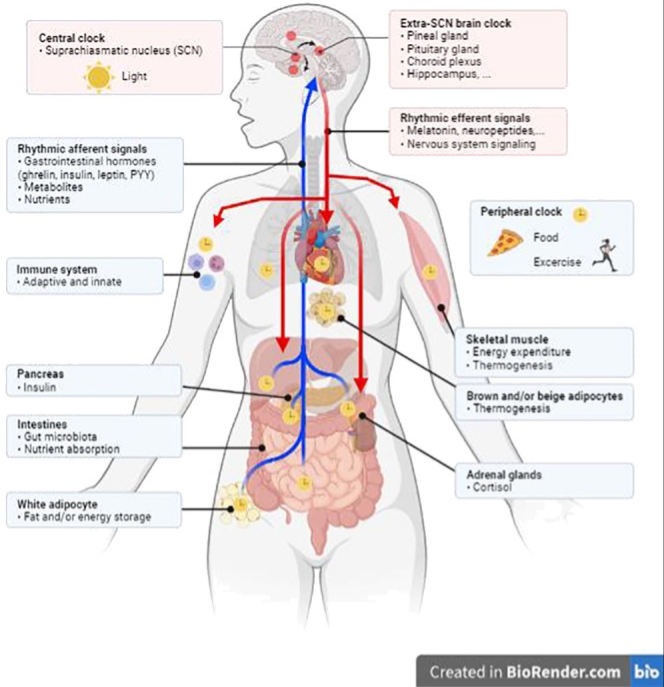
The human body operates on a circadian rhythm, an internal biological clock that regulates various physiological functions over a 24-hour cycle. This rhythm influences sleep, metabolism, hormone release, and cardiovascular activity. Disruptions to the circadian system can have significant health consequences, particularly for metabolism and heart health.
How the Circadian System Works
The
circadian system consists of:
These biological clocks work together to maintain balance in daily activities such as:
✔️ Sleep and wakefulness cycles
✔️ Physical activity regulation
✔️ Food intake timing
✔️ Glucose sensitivity and insulin regulation
✔️ Cardiovascular function
The Link Between Circadian Disruptions and Metabolic Disorders
When the circadian rhythm is disrupted—due to factors like irregular sleep patterns, night shift
work, or frequent time zone changes—it can negatively affect metabolism. Studies have shown
that:
Circadian Rhythms and Cardiovascular Health
The
heart and blood vessels follow a daily rhythm, adjusting blood pressure and heart rate based on
the time of day. Circadian misalignment has been linked to:
How to Maintain a Healthy Circadian Rhythm
To support metabolic and cardiovascular health, consider these science-backed strategies: 🌞 Exposure to natural light: Spend time outdoors during the day to help regulate your internal clock. 🌙 Consistent sleep schedule: Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep per night, going to bed and waking up at the same time daily. 🍽️ Time-restricted eating: Try to align meals with daylight hours, avoiding late-night snacking. 🏋️ Regular physical activity: Exercise during the day rather than late at night for better metabolic function.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy circadian rhythm is essential for overall health, particularly in preventing metabolic disorders and cardiovascular disease. By aligning daily habits with our natural biological clock, we can improve well-being and reduce health risks associated with circadian disruption.